How Do Fish Mate 2
Have you ever wondered how fish mate? It’s a fascinating process full of surprises.
Whether you’re curious about your aquarium friends or just love learning about nature, understanding fish mating can change the way you see these creatures. You’ll discover the different ways fish find partners, their unique behaviors, and why their mating habits matter to the underwater world.
Ready to dive in and uncover the secrets of fish love? Keep reading—you won’t want to miss this!
Fish Mating Basics
Fish reproduce in many interesting ways. Understanding how they mate helps us learn about nature. Fish have unique habits and behaviors during mating. Their methods depend on species and environment.
Mating in fish often involves simple or complex actions. Some fish show bright colors or build nests. Others release eggs and sperm in water. These basics are key to fish reproduction.
Types Of Fish Mating
Fish mating can be divided into two main types: external and internal fertilization. External fertilization is common. Fish release eggs and sperm outside the body. This happens in water, where fertilization occurs.
Internal fertilization is less common. In this type, sperm enters the female’s body. Fertilization happens inside her. Some fish even give live birth, not laying eggs.
Different species use different methods. Some guard their eggs carefully. Others leave eggs to hatch on their own. These types show fish diversity in reproduction.
Environmental Triggers
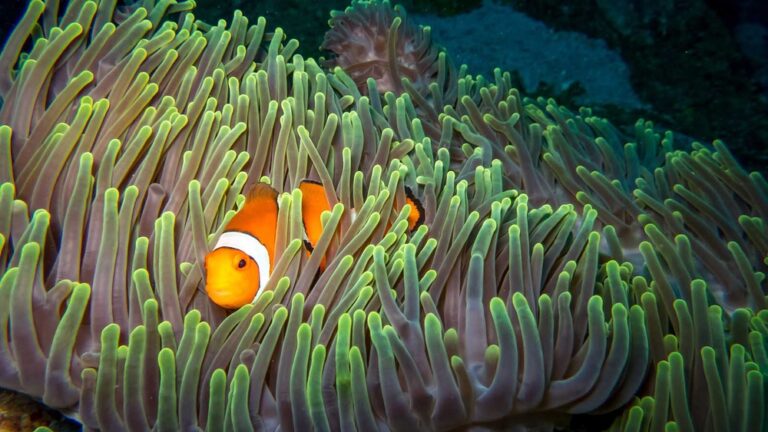
Fish often mate when conditions are right. Water temperature, light, and seasons affect them. Many fish spawn in spring or summer. Warm water helps eggs develop well.
Some fish respond to water flow changes. Rain or flooding can signal mating time. Food availability also plays a role. Fish need energy to reproduce successfully.
Environmental triggers ensure fish mate at the best time. This increases the chance of young fish survival. Nature’s timing is very important for fish reproduction.

Credit: www.aquariadise.com
Spawning Methods
Fish use different ways to reproduce. These ways are called spawning methods. Spawning means releasing eggs and sperm for fertilization. The two main types are external fertilization and internal fertilization. Each method has unique steps and advantages.
External Fertilization
Most fish use external fertilization. The female lays eggs in water. The male then releases sperm over the eggs. Fertilization happens outside the bodies.
This method needs careful timing. Eggs and sperm must meet quickly to fertilize. Many fish lay thousands of eggs to increase chances. The eggs float or stick to plants and rocks. This way, they stay safe until hatching.
Internal Fertilization
Some fish use internal fertilization. The male puts sperm inside the female’s body. Fertilization happens inside her body. This method protects the eggs better.
Fish that use internal fertilization often give birth to live young. Others keep eggs inside until they hatch. This method lowers the risk from predators and the environment.
Courtship Behaviors
Fish use special courtship behaviors to find and attract mates. These behaviors help fish choose the best partners and prepare for mating. Fish rely on different signals to communicate during courtship. They use sight, smell, and actions to show their readiness.
Visual Displays
Many fish use bright colors and movements to attract mates. Males often show vivid patterns or change colors. They swim in unique ways to catch the female’s eye. These displays show health and strength. Clear, sharp movements help convince mates of their quality.
Chemical Signals
Fish release chemicals called pheromones in the water. These signals tell others about their readiness to mate. Females can sense the strongest males through smell. Pheromones also help synchronize mating times. This chemical communication works even in murky water.
Nesting Rituals
Some fish build nests to attract mates and protect eggs. Males often create or clean these spaces. They show their ability to care for offspring. Nesting also provides a safe place for fertilization. Females choose mates based on the quality of these nests.
Egg Laying And Care
Fish reproduce by laying eggs, a process that involves careful selection of safe places and sometimes active care. Egg laying and care vary among species but share key steps. These steps ensure eggs develop safely until hatching.
Egg Deposition Sites
Fish choose special spots to lay eggs. These can be plants, rocks, or the ocean floor. Some fish dig small nests in the sand or mud. The choice depends on safety from predators and water conditions. Clean, oxygen-rich water helps eggs survive. Some species lay eggs in hidden places to avoid danger.
Parental Protection
Many fish protect their eggs after laying them. Some stay close to guard the eggs from predators. Others fan water over the eggs to keep them clean and oxygenated. Mouthbrooders carry eggs in their mouths until they hatch. This care increases the chance of survival for the young fish.
Hatching Process
Eggs hatch after days or weeks, depending on the fish type and water temperature. The baby fish, called fry, break free using a small egg tooth. Fry are very small and weak at first. They often stay near the safe site until strong enough to swim and find food.
Mating Variations Among Species
Fish show many ways to mate. Each species has unique habits. These differences help them survive in different environments. Understanding these methods reveals nature’s creativity in reproduction.
Fish mating styles often depend on their biology. Some give birth to live young. Others lay eggs in hidden places. Some even protect their eggs in their mouths. A few species change sex to mate better.
Livebearers Vs. Egg Layers
Livebearers keep their young inside until birth. They give birth to small, active fish. Guppies and mollies are common livebearers. Egg layers lay eggs outside their bodies. They often hide eggs in plants or rocks. Many tropical fish use this method.
Mouthbrooders
Mouthbrooders carry eggs or young in their mouths. This protects the offspring from predators. Some hold eggs until they hatch. Others keep young fish safe after birth. Cichlids are famous mouthbrooders. This method increases baby fish survival.
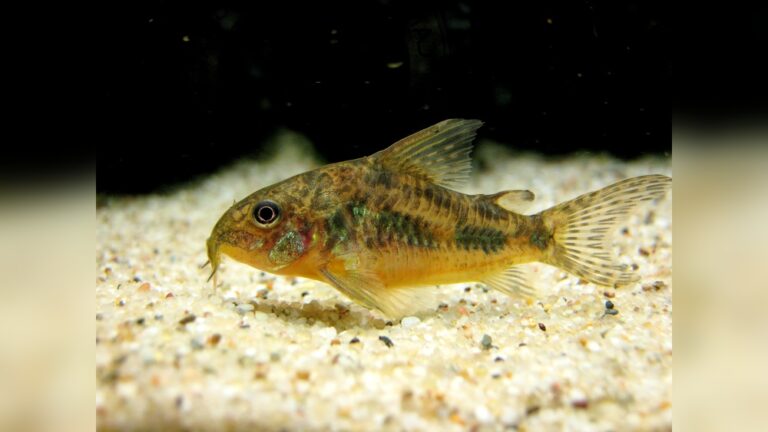
Hermaphroditic Fish
Some fish can be male and female. They change sex based on social needs. Clownfish start as males and become females. This helps them find mates easily. Hermaphroditism ensures mating chances in small groups.

Credit: www.walmart.com
Impact Of Environment On Mating
The environment plays a big role in how fish mate. Fish depend on many natural factors to start and complete mating. Changes in their surroundings can help or stop this process. Understanding these effects helps us protect fish and their habitats.
Water Temperature
Water temperature affects fish mating directly. Many fish need specific temperatures to begin spawning. Warm water can speed up mating behavior. Cold water often slows it down or stops it completely. Some fish travel to warmer areas to lay eggs. Temperature changes can also affect the development of fish eggs.
Seasonal Changes
Seasons control when fish mate. Many fish spawn in spring or summer. Longer daylight and warmer water trigger mating instincts. Seasonal changes ensure eggs hatch when food is abundant. Fish follow these natural cycles to increase survival rates. Disrupting these cycles can confuse fish and reduce mating success.
Pollution Effects
Pollution harms fish mating in many ways. Chemicals in water can change fish hormones. This affects their ability to find mates or produce eggs. Trash and waste can destroy breeding spots. Polluted water can also kill young fish before they grow. Protecting water quality is key to healthy fish populations.
Credit: closerpets.co.uk
How Smart Pets Lover Can Help You with How Do Fish Mate 2
Exploring Fish Mating Through Hands-On Learning
Understanding fish mating goes beyond just reading about courtship behaviors or spawning methods; it’s about observing and appreciating these natural wonders firsthand. Whether you keep a small aquarium or simply enjoy visiting local ponds, paying close attention to egg laying and care patterns can reveal fascinating insights into how different species nurture their young.
For pet parents eager to deepen their knowledge, creating a controlled environment that mimics natural conditions can be a practical learning opportunity. This helps highlight the impact of environment on mating success, reinforcing how crucial water quality, temperature, and habitat structure are for healthy fish reproduction.
- Set up a dedicated breeding tank with proper filtration and plants.
- Document courtship rituals and note species-specific behaviors.
- Observe variations in mating strategies among different fish types.
At Smart Pets Lover, we believe that every moment spent learning about your aquatic companions strengthens your connection and care. If you ever want to chat about fish behavior or need guidance on creating an ideal breeding setup, reaching out to knowledgeable communities or local experts can be incredibly helpful. After all, where every wag, purr, and chirp tells a story, every splash and swim has its own tale to share too.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Fish Reproduce In Water?
Fish reproduce by external fertilization, where females lay eggs and males release sperm over them. This process occurs in water, ensuring eggs are fertilized and develop safely.
What Are The Common Mating Behaviors Of Fish?
Fish show various mating behaviors like nest building, courtship dances, and vocalizations. These actions help attract mates and increase the chances of successful reproduction.
Do All Fish Species Mate The Same Way?
No, fish species have diverse mating methods. Some lay eggs externally, others give birth to live young, and some practice mouthbrooding for protection.
How Long Does Fish Mating Last?
Fish mating duration varies by species. It can last from a few seconds during spawning to several hours in species with elaborate courtship rituals.
Conclusion
Fish have many ways to mate and reproduce. Some lay eggs, while others give live birth. Mating habits depend on the species and environment. Understanding these behaviors helps us appreciate nature better. Fish mating is a fascinating part of life underwater.
Watching how fish care for their young is inspiring. Nature’s diversity shows us many unique survival strategies. Keep exploring to learn more about aquatic life.






