Diy Aquarium Projects For Biology Students
Are you a biology student looking for a fun and hands-on way to explore aquatic life? DIY aquarium projects can be the perfect solution.
Not only will you get to build and customize your own mini ecosystem, but you’ll also gain valuable insights into biology concepts like ecosystems, water chemistry, and animal behavior. Imagine watching your aquarium come to life while learning at the same time.
Keep reading to discover simple and exciting projects that will make your studies more engaging and memorable. Your next biology breakthrough might just start with a tank!
Choosing The Right Aquarium
Choosing the right aquarium is the first step in any DIY project for biology students. The aquarium must suit the type of study and the species involved. A well-chosen tank helps students observe aquatic life closely and safely.
Consider size, material, and location carefully. These factors affect water quality, animal health, and ease of maintenance. Thoughtful choices make the project more successful and enjoyable.
Selecting Tank Size
Tank size depends on the species and number of animals. Small tanks suit tiny fish or invertebrates. Larger tanks provide more space and stability for bigger species.
Start with at least 5 gallons for beginners. This size is easier to clean and manage. Bigger tanks need more water and power but offer better living conditions.
Material Options
Glass and acrylic are common materials for aquariums. Glass is clear and scratch-resistant. Acrylic is lighter and less likely to break.
Choose glass for a budget-friendly option. Acrylic works well for large or custom shapes. Both materials keep water safely inside and show aquatic life well.
Location Tips
Place the aquarium on a strong, flat surface. Avoid direct sunlight to prevent overheating and algae growth. Keep it away from heaters or vents.
Pick a quiet place with easy access for feeding and cleaning. A good spot helps maintain stable water conditions and reduces stress for the animals.
Essential Equipment Setup
Setting up the right equipment is key for a successful DIY aquarium project. Biology students need to create a healthy space for fish and plants. Essential tools control water quality, light, and temperature. Each piece plays a role in the aquarium’s balance.
Choosing the right equipment can help students observe real-life biology concepts. It also ensures the aquarium stays clean and safe. Understanding these basics is the first step in building a thriving aquatic environment.
Filtration Systems
Filtration keeps the water clean and clear. It removes waste and harmful chemicals. A good filter supports fish health and growth. There are three main types: mechanical, biological, and chemical filters. Mechanical filters trap debris. Biological filters use beneficial bacteria to break down waste. Chemical filters remove toxins and odors. Choose a filter that fits the tank size and type of fish. Regular cleaning and maintenance keep the filter working well.
Lighting Choices
Proper lighting helps plants grow and fish stay active. LED lights are popular due to low energy use. They produce less heat and last long. Some lights mimic natural sunlight, which supports photosynthesis in plants. Avoid lights that are too bright or too dim. Timers can control light cycles, simulating day and night. This helps create a natural rhythm in the aquarium. Choose lights based on the plants and animals in the tank.
Heating And Temperature Control
Many fish need stable temperatures to thrive. A heater keeps water warm in cooler rooms. Use a thermometer to monitor water temperature. Set the heater to the correct range for your fish species. Sudden temperature changes can stress or harm fish. Heaters come in different sizes for various tank volumes. Some have built-in thermostats for easy control. Keep the heater fully submerged for safety and efficiency.
Creating Aquatic Habitats
Building an aquatic habitat is a rewarding project for biology students. It offers hands-on experience with living ecosystems. Students learn about water chemistry, plant life, and aquatic animals. Creating a balanced environment is key for healthy aquatic life.
Understanding different tank types and their needs helps students design suitable habitats. This knowledge supports studying aquatic biology in a real-world context. It also encourages responsibility and careful observation skills.
Freshwater Vs Saltwater Tanks
Freshwater tanks are easier to maintain and cost less. They support many common fish and plants. Saltwater tanks need special salt mixes and careful monitoring. They house more diverse creatures like corals and marine fish.
Choosing between these depends on the study goals and resources. Freshwater tanks are great for beginners. Saltwater tanks offer a deeper look into marine ecosystems.
Plant Selection And Care
Plants improve water quality by absorbing waste. Choose plants that fit the tank type and size. Fast-growing plants reduce algae growth. Some plants need strong light; others prefer low light.
Regular trimming keeps plants healthy and prevents overcrowding. Use fertilizers designed for aquatic plants. Monitor plant health to adjust care as needed.
Substrate And Decoration Ideas
Substrate supports plant roots and provides shelter for animals. Sand, gravel, and soil are common options. Select substrate based on plant types and tank inhabitants.
Decorations like rocks and driftwood add hiding places and interest. Avoid sharp objects that may harm fish. Natural decorations create a more realistic environment for study.

Credit: www.steampoweredfamily.com
Water Quality Management
Water quality management is key in any aquarium project. It helps keep fish and plants healthy. Good water quality prevents diseases and keeps the environment stable. Biology students learn a lot by managing water quality in their DIY aquariums.
Testing Water Parameters
Testing water parameters shows the health of the aquarium water. Measure ammonia, nitrite, nitrate, and oxygen levels. Use simple test kits for accurate results. Test water weekly to catch problems early. Record results to track changes over time.
Maintaining Ph And Hardness
pH and hardness affect fish and plant survival. Most freshwater fish prefer pH between 6.5 and 7.5. Use pH test strips to check regularly. Hardness measures minerals like calcium and magnesium. Adjust hardness with aquarium salts or water changes. Keep these levels steady for a balanced tank.
Regular Cleaning Routines
Cleaning keeps water clear and safe. Change 10-20% of the water weekly. Remove uneaten food and debris from the tank. Clean filters monthly but avoid harsh chemicals. Use a gravel vacuum to clean the substrate. Regular care reduces harmful bacteria and toxins.
Selecting Aquatic Species
Selecting the right aquatic species is key for a successful DIY aquarium project. Biology students need species that are easy to care for and help with learning. The choice affects tank setup, water conditions, and maintenance. Understanding each species’ needs leads to a healthy, balanced aquarium.
Fish Suitable For Students
Small fish like guppies and bettas are great for beginners. They need simple care and adapt well to tank life. Goldfish are also popular but require larger tanks. These fish show clear behaviors, making them good for study. They survive in a range of water conditions.
Invertebrates And Amphibians
Snails and shrimp add diversity and help keep the tank clean. They are easy to care for and interesting to observe. Frogs and newts can also be included but need specific environments. These species provide insight into different aquatic life forms. They require careful attention to water quality.
Compatibility And Behavior
Choosing species that get along reduces stress and aggression. Some fish are territorial and do not mix well with others. Research the behavior of each species before adding them. Group fish with similar temperaments and water needs. A peaceful community tank is easier to maintain and study.
Credit: www.milkwood.net
Scientific Experiments In Aquariums
Aquariums offer a unique space for biology students to conduct scientific experiments. These controlled environments mimic natural habitats, making them ideal for observing living organisms. Students can explore various biological concepts through hands-on activities. Scientific experiments in aquariums help students understand animal behavior, water quality, and ecosystem balance.
Monitoring Growth And Behavior
Tracking the growth of fish or plants in an aquarium shows how living things develop. Students can measure size changes and note physical differences over time. Observing behavior reveals how animals react to different stimuli. For example, students can study feeding habits or social interactions. These observations provide valuable data for biology projects.
Water Chemistry Experiments
Water quality affects all life in the aquarium. Testing pH levels, temperature, and oxygen content helps students learn about water chemistry. They can experiment with changes in water conditions and record effects on fish and plants. This practice teaches important lessons about environmental science and pollution. Students gain skills in using scientific tools and data analysis.
Ecosystem Observation Projects
Aquariums are small ecosystems with many living parts. Students can observe how plants, fish, and microorganisms interact. They can study nutrient cycles and energy flow within this system. Watching how changes affect the ecosystem helps students understand balance and sustainability. These projects build a strong foundation in ecology and environmental biology.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Building and maintaining a DIY aquarium is a rewarding project for biology students. Problems can arise that may affect the health of fish and plants. Knowing how to fix common issues keeps the aquarium healthy and thriving. Troubleshooting helps students learn and enjoy their project more.
Algae Control
Algae can grow fast and cover the tank surfaces. It makes the aquarium look dirty and harms plants. Use less light and avoid direct sunlight. Clean the glass and decorations regularly with a soft brush. Add algae-eating fish or snails to help control growth naturally. Test water for excess nutrients like nitrates and phosphates, which feed algae. Change water often to keep it clean.
Disease Prevention
Fish can get sick from poor water or overcrowding. Always quarantine new fish before adding them to the tank. Keep water clean with regular changes. Avoid overfeeding, which pollutes the water. Watch fish daily for signs of illness like spots, swelling, or strange swimming. Remove sick fish quickly to prevent spread. Use medicines only when necessary and follow instructions carefully.
Equipment Failures
Filters, heaters, and lights may stop working suddenly. Check equipment regularly to ensure it runs smoothly. Have spare parts or backup devices ready. Clean filters to avoid clogging. Use a thermometer to monitor water temperature. Replace bulbs when they get dim. Fix or replace broken equipment immediately to avoid harm to aquarium life.
Budget-friendly Project Tips
Building an aquarium project does not have to be expensive. Biology students can save money with smart choices. Budget-friendly tips help create a great learning tool without spending too much. These tips focus on using affordable materials and easy maintenance.
Diy Equipment Hacks
Make your own equipment to cut costs. Use household items like plastic containers for water filters. A small air pump can be replaced with a battery-powered fan. DIY heaters can be made using safe, low-wattage bulbs. Simple lighting setups with LED strips save energy and money.
Reusing Materials
Reuse old jars, bottles, or containers as fish tanks or decorations. Broken aquarium parts can be repaired or repurposed. Use stones and plants from outside instead of buying new ones. Cardboard or wood scraps make good backgrounds or stands. Recycling materials lowers expenses and helps the environment.
Cost-effective Maintenance
Keep maintenance costs low by feeding fish small amounts to reduce waste. Change only part of the water regularly to save on water and chemicals. Use natural cleaning methods like rinsing filter sponges in tank water. Choose hardy fish and plants that need less care. Prevent problems by monitoring water quality often.
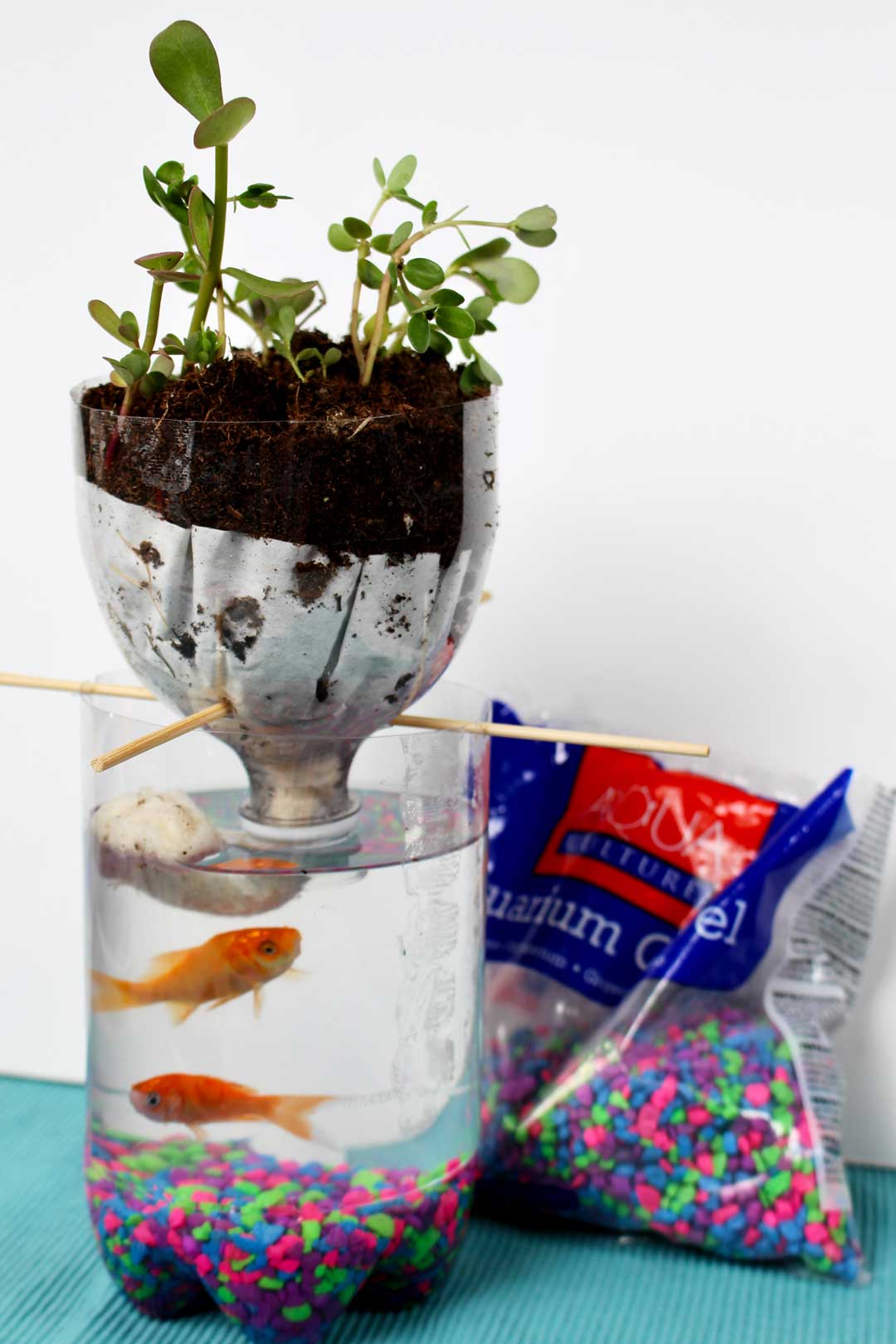

Credit: welcometonanas.com
How Smart Pets Lover Can Help You with Diy Aquarium Projects For Biology Students
Bringing Biology Lessons to Life Through DIY Aquariums
For biology students, DIY aquarium projects offer more than just a fun hobby—they’re a hands-on gateway to understanding aquatic ecosystems. By carefully selecting the right aquarium and mastering essential equipment setup, students can create realistic aquatic habitats that mirror natural environments. This practical approach deepens learning about water quality management and species behavior, turning textbook concepts into living experiments.
Engaging with these projects nurtures responsibility and curiosity, reflecting the thoughtful care that every pet parent appreciates. It’s about connecting with life on a deeper level, much like how Smart Pets Lover encourages emotional bonds with animals through informed care. Whether troubleshooting common issues or exploring budget-friendly tips, these aquariums become vibrant classrooms where science truly swims off the page.
For additional guidance or questions, biology students and enthusiasts can find valuable resources and community support by reaching out to local aquarium clubs or educational forums. Learning never stops when curiosity leads the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Materials Are Needed For Diy Aquarium Projects?
Basic materials include a glass or acrylic tank, water pump, filter, substrate, plants, and decorations. Biology students may also need water testing kits and aquatic organisms for study.
How Can Diy Aquariums Benefit Biology Students?
DIY aquariums provide hands-on learning about aquatic ecosystems, water chemistry, and organism behavior. They enhance observation skills and practical understanding of biology concepts.
What Are Easy Diy Aquarium Setups For Beginners?
Simple setups include betta fish tanks, shrimp tanks, or planted freshwater tanks. These require minimal equipment and are manageable for biology students new to aquariums.
How To Maintain Water Quality In Diy Aquariums?
Regular water changes, proper filtration, and monitoring pH and ammonia levels are key. Good maintenance ensures a healthy environment for aquatic life.
Conclusion
Creating DIY aquarium projects helps biology students learn actively. These projects make science fun and hands-on. Students observe fish behavior and water life closely. Building aquariums teaches patience and care for living things. Small steps lead to big discoveries in biology.
Experimenting with setups shows how ecosystems work. Such projects boost curiosity and critical thinking skills. Biology feels real, not just words in books. Try simple projects to start your learning journey. Keep exploring and enjoy the wonders of aquatic life.