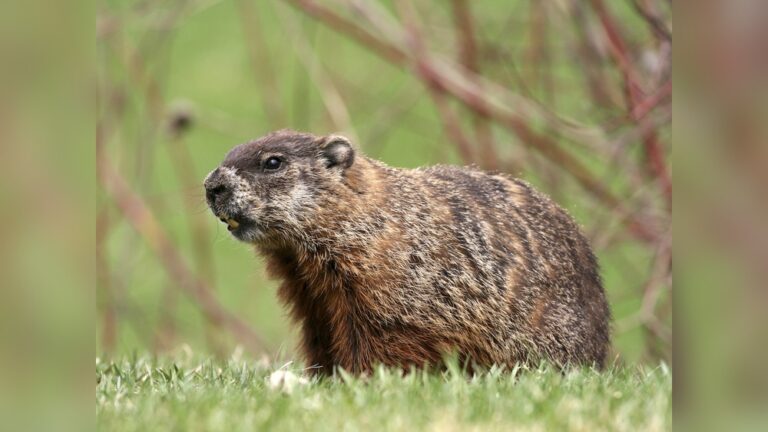
Chipmunk Vs Ground Squirrel: Key Differences You Must Know
Have you ever spotted a small, striped animal darting through your backyard and wondered if it’s a chipmunk or a ground squirrel? These two creatures look quite similar but have some surprising differences that affect how they live and behave.
Knowing which one you’re dealing with can change how you protect your garden or enjoy watching wildlife. Keep reading, and you’ll discover the key traits that set chipmunks and ground squirrels apart—helping you tell them apart easily the next time you see one.
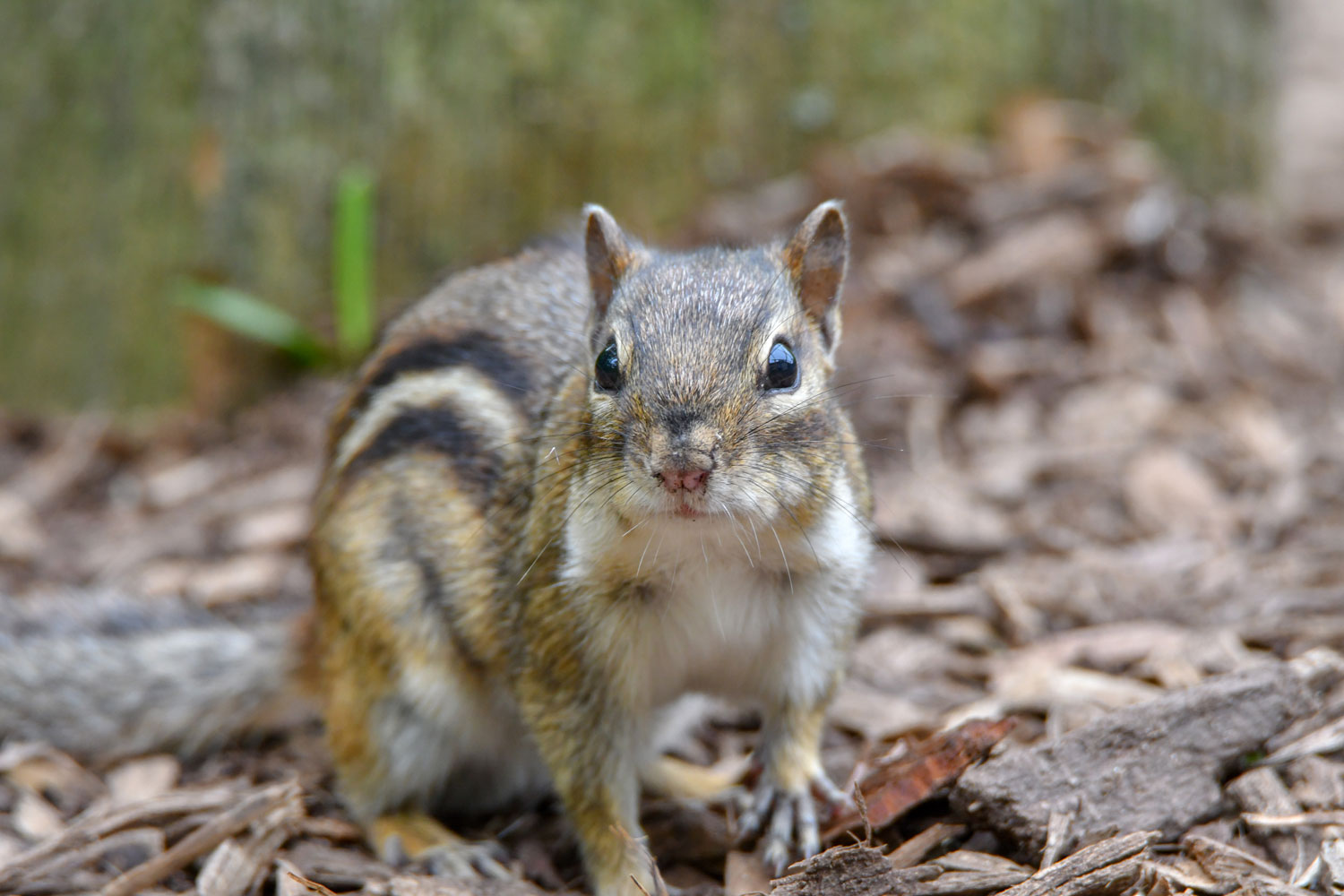

Credit: www.reconnectwithnature.org
Physical Traits
Physical traits help us tell chipmunks and ground squirrels apart. Both are small rodents, but they look quite different. Their size, fur, and tails show clear signs. These signs help us identify each animal in nature easily.
Understanding these traits also helps in studying their behavior and habitats. Let’s explore their physical differences in detail.
Size And Build
Chipmunks are smaller and slimmer. They usually measure about 5 to 6 inches long. Their bodies are light and quick. Ground squirrels are larger and more robust. They can grow up to 10 inches. They have thicker legs and a stockier body.
Fur Patterns
Chipmunks have distinct stripes on their backs. These stripes run from head to tail. The stripes are dark with light borders. Ground squirrels have less clear stripes or none at all. Their fur is mostly one color, like brown or gray. This helps them blend into the ground and rocks.
Tail Characteristics
Chipmunks have fluffy, bushy tails. Their tails are often held upright. Ground squirrels have shorter and less bushy tails. They keep their tails low or flat on the ground. This difference is easy to spot when they move.
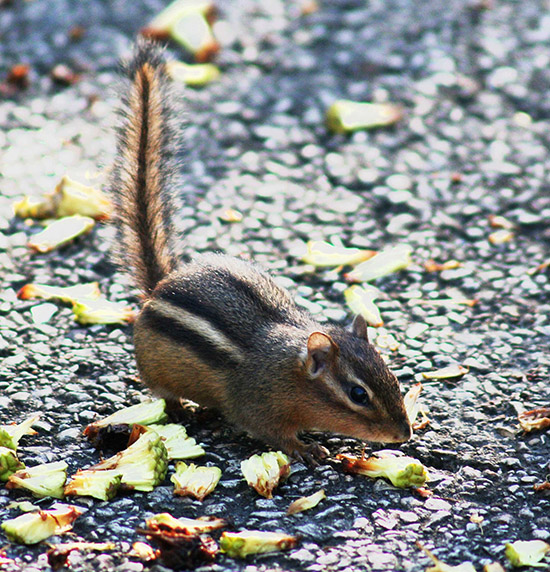

Credit: hyg.ipm.illinois.edu
Habitat And Range
Understanding the habitat and range of chipmunks and ground squirrels helps us see how these animals live. Their homes and where they roam show their needs and habits. Both animals share some environments but also prefer different places to thrive.
Preferred Environments
Chipmunks like forests with plenty of trees and bushes. They often live near rocks or logs for hiding. These small animals build nests underground or in tree roots. They enjoy places with lots of cover and food like nuts and berries.
Ground squirrels prefer open areas like grasslands and fields. They dig large burrows in soil to live and store food. These squirrels need space to run and look out for predators. They thrive in sunny places with short grass and few trees.
Geographical Distribution
Chipmunks mostly live in North America, especially in the United States and Canada. Some species also appear in parts of Asia. They usually stay in wooded or mountainous regions.
Ground squirrels also live mainly in North America. They are common in the western U.S. and parts of Mexico. Some species live in open plains and deserts, adapting well to dry climates.
Behavioral Habits
Chipmunks and ground squirrels show different behaviors in their daily lives. These habits help them survive in the wild. Understanding their behavior can help you tell them apart easily.
Activity Patterns
Chipmunks are mostly active during the day. They spend much time gathering food and exploring. Ground squirrels are also active in daylight. They rest during the hottest hours. Both animals avoid night activity to stay safe from predators.
Social Structure
Chipmunks prefer to live alone. Each chipmunk has its own territory. They may become aggressive if others enter their space. Ground squirrels are more social animals. They live in groups called colonies. This helps protect them from danger.
Burrowing And Nesting
Chipmunks dig small burrows with many tunnels. They store food inside for winter. Their nests are lined with leaves and grass. Ground squirrels create larger burrows with several entrances. These burrows are shared with family members. They use them for shelter and raising young.

Credit: www.thinkwildco.org
Diet And Feeding
Chipmunks and ground squirrels have different eating habits. Their diets show how they live and survive in the wild. Understanding what they eat helps us see their role in nature.
Primary Food Sources
Chipmunks mostly eat seeds, nuts, and fruits. They also enjoy insects and small plants. Their diet changes with the seasons. In spring and summer, they eat more insects. In fall, they gather nuts to store for winter.
Ground squirrels eat more variety. They feed on grass, roots, and seeds. Sometimes, they eat insects and eggs. Their diet depends on the area they live in. They eat what is easy to find around them.
Foraging Techniques
Chipmunks are quick and careful foragers. They search on the ground and in low bushes. They use their sharp teeth to crack open nuts. They carry food in their cheek pouches to store later.
Ground squirrels dig for roots and bulbs. They also pick seeds from plants. They are active during the day, searching in open areas. Their strong claws help them dig holes to find food.
Communication Styles
Chipmunks and ground squirrels use different ways to talk to each other. Their communication styles help them stay safe, find food, and build social bonds. Understanding these styles reveals how these animals live and survive in the wild.
Vocalizations
Chipmunks make sharp, high-pitched sounds. These calls warn about danger or mark their territory. Their chirps can be fast or slow, showing different messages.
Ground squirrels produce louder and deeper sounds. Their calls often serve as alarms for predators nearby. Some ground squirrels whistle to alert their group quickly.
Body Language
Chipmunks use tail flicks and head movements. These gestures signal alertness or friendliness. A twitching tail can mean the chipmunk feels threatened.
Ground squirrels stand tall on their hind legs. This posture helps them watch for threats. They also use tail waving to warn others or show submission.
Reproduction And Lifespan
Reproduction and lifespan are key to understanding chipmunks and ground squirrels. These small mammals have unique ways of mating, caring for their young, and living through the years. Their life cycles affect their behavior and survival in nature.
Mating Season
Chipmunks usually mate in early spring. The season lasts a few weeks only. Ground squirrels start mating slightly later, in mid to late spring. Both species are ready to breed once a year. Mating is short and often secretive to avoid predators.
Offspring Care
Chipmunk mothers build nests underground. They care for their babies until they are strong. Baby chipmunks stay in the nest for about two months. Ground squirrel mothers also raise young in burrows. They keep their pups safe and warm. Both species teach their young to find food before leaving.
Average Lifespan
Chipmunks live around 2 to 3 years in the wild. Some can live up to 8 years in safe conditions. Ground squirrels have a similar lifespan, averaging 3 to 4 years. Predators and weather often shorten their lives. Both animals must reproduce quickly to keep their numbers steady.
Role In Ecosystem
Chipmunks and ground squirrels play important roles in their ecosystems. Both animals help keep the environment balanced. They affect plants and animals around them in different ways. Understanding their roles shows how nature stays healthy.
These small mammals are more than just cute creatures. They are active participants in their habitats. Their actions shape the land and support other wildlife.
Impact On Vegetation
Chipmunks and ground squirrels feed on seeds, nuts, and plants. This helps spread seeds across the area. They often bury food, which can grow into new plants. This natural planting helps forests and grasslands thrive.
They also eat parts of plants, which controls plant growth. This prevents some plants from taking over too much space. Their digging loosens soil, allowing air and water to reach roots better.
Predator-prey Relationships
These animals serve as food for many predators. Hawks, foxes, and snakes hunt them regularly. This keeps predator populations stable and healthy. Chipmunks and ground squirrels help support the food chain.
They stay alert and quick to avoid danger. Their presence affects predator behavior and hunting patterns. This interaction balances the numbers of animals in the ecosystem.
Common Misconceptions
Many people confuse chipmunks with ground squirrels. These small animals share some looks but have clear differences. Understanding these differences helps avoid mix-ups.
People often think chipmunks live only in trees. Actually, they spend much time on the ground. Ground squirrels also live underground but have different burrow styles.
Misunderstanding Their Size
Chipmunks are smaller than ground squirrels. Chipmunks usually measure 5 to 6 inches long. Ground squirrels can grow up to 12 inches. Size helps tell them apart easily.
Confusing Their Sounds
Chipmunks make high-pitched chirps. Ground squirrels produce louder, harsher calls. Their sounds serve different purposes like warnings or communication.
Mistaking Their Habitats
Chipmunks prefer forests and wooded areas. Ground squirrels live in open fields and grasslands. Habitat choice is a key difference between them.
Assuming They Have The Same Diet
Chipmunks eat nuts, seeds, and fruits mostly. Ground squirrels also eat insects and small animals. Their diets overlap but are not identical.
How Smart Pets Lover Can Help You with Chipmunk Vs Ground Squirrel
Learning From Chipmunks and Ground Squirrels: Practical Insights for Curious Pet Parents
Understanding the subtle differences between chipmunks and ground squirrels opens up more than just trivia—it’s a wonderful opportunity to deepen our connection with nature. Observing their behavioral habits and communication styles, for instance, can inspire us to appreciate the unique ways animals interact with their environment and each other. This awareness helps pet parents recognize the importance of habitat and range, encouraging responsible outdoor practices that protect wildlife.
At Smart Pets Lover, we believe every animal story enriches our bond with the natural world. When you spot these little critters, take a moment to notice their physical traits and feeding habits; it’s a simple yet meaningful way to nurture curiosity and empathy. For more thoughtful insights and research-backed tips on animal behavior, feel free to reach out to our team. After all, where every wag, purr, and chirp tells a story, learning never stops.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Main Differences Between Chipmunks And Ground Squirrels?
Chipmunks have distinctive stripes on their faces and bodies, while ground squirrels have less defined markings. Chipmunks are smaller and often live in burrows, whereas ground squirrels are larger and inhabit open areas. Their behaviors and habitats vary significantly.
How Can You Identify A Chipmunk Versus A Ground Squirrel?
Chipmunks have cheek pouches and stripes extending to their faces. Ground squirrels have rounder bodies and less pronounced facial stripes. Observing size, habitat, and markings helps differentiate them easily.
Do Chipmunks And Ground Squirrels Have Different Diets?
Both eat seeds, nuts, and fruits, but chipmunks also consume insects and small animals. Ground squirrels mainly focus on plants and grains. Their diets reflect their habitat and activity patterns.
Where Do Chipmunks And Ground Squirrels Typically Live?
Chipmunks prefer wooded or forested areas with dense cover. Ground squirrels are found in open fields, grasslands, and rocky areas. Their homes, like burrows and tunnels, suit their environment.
Conclusion
Chipmunks and ground squirrels share many traits but have clear differences. Chipmunks are smaller with stripes on their faces and backs. Ground squirrels tend to be larger and less colorful. Both live in burrows and gather food for winter. Knowing these facts helps you spot them easily outdoors.
Nature shows us variety in small animals. Each one plays a role in the environment. Watching them can bring simple joy and learning. Keep exploring and enjoy wildlife around you!