Are Bats Rodents: Debunking Common Myths and Surprising Facts
Have you ever wondered if bats are rodents? It’s a question that might surprise you, especially since bats and rodents share some similar features.
You might picture bats as small, furry creatures like mice, but are they really the same? Understanding the truth can change the way you think about these mysterious night flyers. Keep reading, and you’ll uncover fascinating facts that clear up the confusion once and for all.
Your curiosity is about to be rewarded!

Credit: www.jcehrlich.com
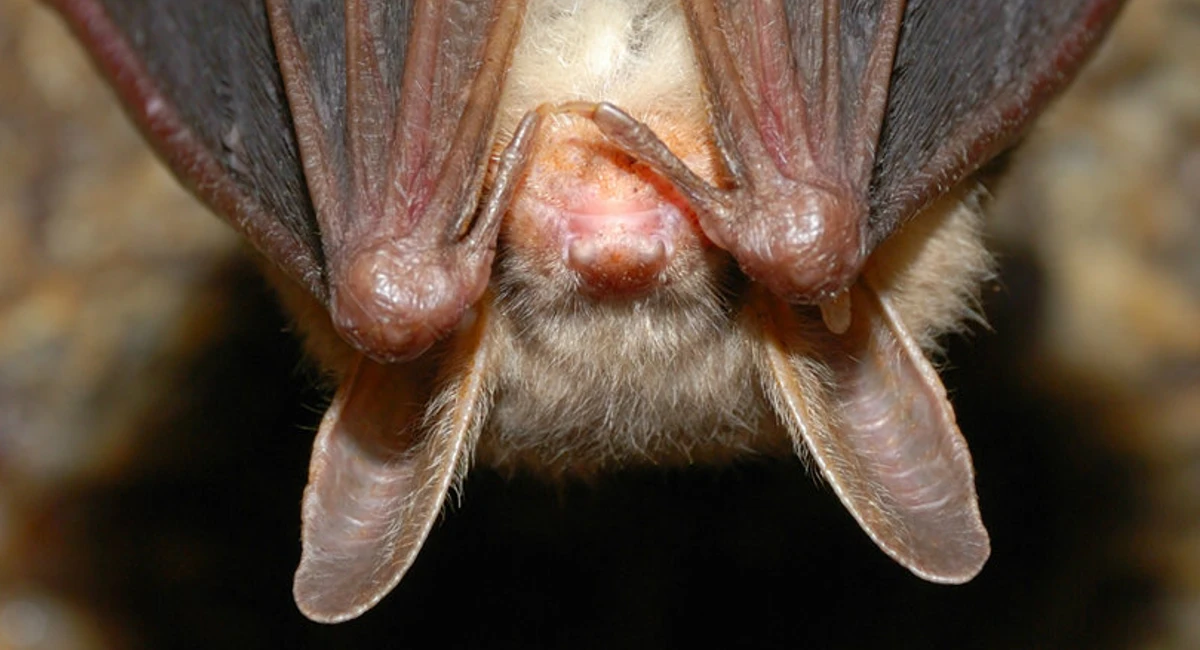
Bat Classification
Bats have a unique place in the animal kingdom. Many people wonder if bats are rodents. Understanding their classification clears up this confusion. Bats belong to a different group than rodents.
Exploring their classification helps us see how bats differ from other mammals. It shows their special traits and why they are not rodents.
Mammal Group
Bats are mammals. They have fur and feed their young with milk. Like other mammals, bats are warm-blooded. They breathe air and have a backbone. These traits place them firmly in the mammal group.
Order Chiroptera
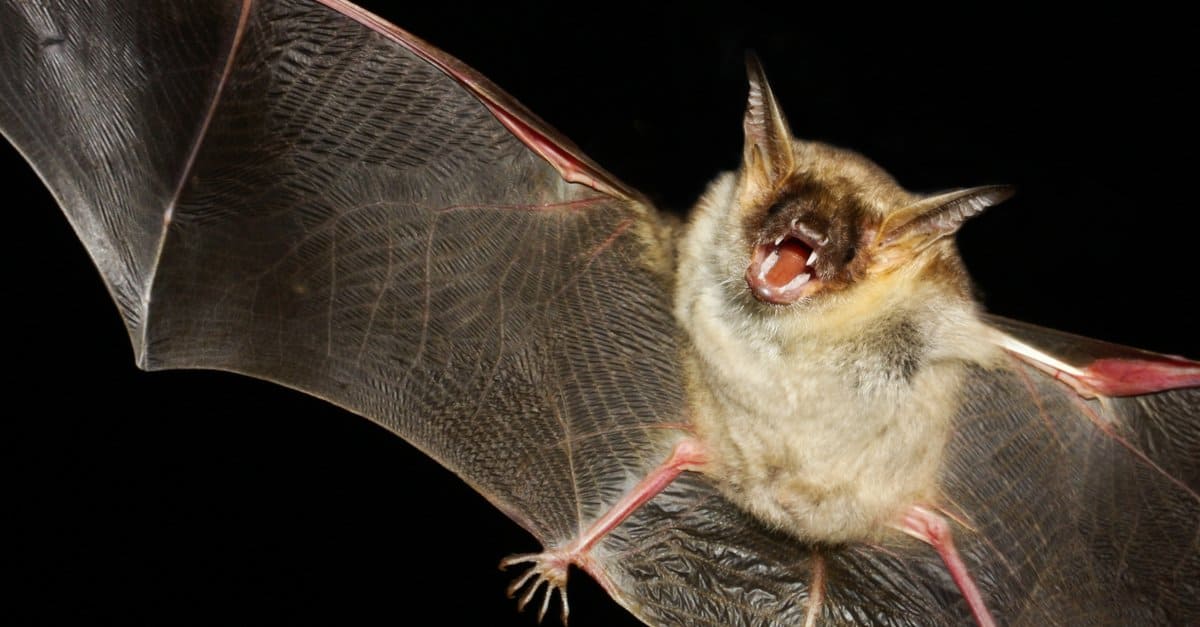
Bats belong to the order Chiroptera. This order means “hand wing.” It describes their wings, which are actually modified hands. This makes bats the only mammals that can truly fly. Chiroptera includes over 1,400 species of bats worldwide.
Differences From Rodents
Rodents and bats are very different. Rodents belong to the order Rodentia. They have strong front teeth for gnawing. Bats do not have these teeth. Instead, bats use echolocation to navigate and find food. Rodents mostly walk or run, but bats fly. These clear differences show bats are not rodents.
Rodent Characteristics
Rodents are a large group of mammals with unique features. These features help identify them easily. Understanding these traits clarifies if bats are rodents.
Rodents have specific physical and behavioral traits. These traits define their place in the animal world.
Teeth Structure
Rodents have sharp, chisel-like front teeth. These teeth grow continuously throughout their life. They use these teeth to gnaw on food and objects. The gap between front and back teeth helps them chew well. This teeth structure is key to rodents’ survival.
Common Rodent Species
Rodents include mice, rats, squirrels, and beavers. These species live in many habitats worldwide. Each species has adapted to its environment well. They share common traits but differ in size and behavior. Knowing common species helps spot rodent features.
Behavior Traits
Rodents are mostly active during the night or twilight. They are good climbers and diggers. Many live in burrows or nests made from twigs and leaves. Rodents often store food for later use. Their behavior shows their need to survive and adapt.
Myths About Bats
Bats have long been surrounded by myths and confusion. Many people wrongly believe bats are rodents. These myths affect how people see and treat bats. Clearing up these wrong ideas helps us understand bats better.
Why Bats Are Mistaken For Rodents
Bats share some features with rodents. Both are small mammals with fur. They also live in dark places like caves or attics. These similarities make people think bats are rodents. The truth is, bats belong to their own group called Chiroptera.
Popular Misconceptions
Some think bats are blind or dirty. Others believe bats spread diseases easily. Many imagine bats as flying mice. None of these ideas are fully true. Bats have good eyesight and clean themselves often. They play important roles in nature, like eating insects and pollinating plants.
Origins Of These Myths
Old stories and movies spread wrong ideas about bats. Their night activity and strange sounds cause fear. Lack of knowledge also adds to myths. People pass these myths from one generation to the next. Science shows bats are very different from rodents and are helpful animals.
Unique Bat Features
Bats have many unique features that set them apart from rodents and other animals. These features help bats survive and thrive in different environments. Understanding these traits shows how special bats really are.
They are not just flying rodents. Their abilities and habits are quite distinct.
Flight Abilities
Bats are the only mammals capable of true flight. Their wings are made of a thin membrane stretched over long fingers. This design allows precise and agile movements in the air. Bats can hover, glide, and quickly change direction while flying. These skills help them catch insects and avoid predators.
Echolocation
Bats use echolocation to navigate and find food in the dark. They emit high-pitched sounds that bounce off objects. The returning echoes tell bats about the location, size, and shape of things around them. This ability works like a natural radar. It helps bats fly safely and hunt at night.
Diet And Habitat
Bats eat a wide range of foods. Many species consume insects, while others feed on fruit, nectar, or even small animals. They live in diverse habitats like caves, forests, and buildings. Bats adapt well to different environments, making them important for ecosystems. Their diet controls insect populations and helps pollinate plants.
Ecological Importance
Bats play a vital role in nature. They help balance many parts of the ecosystem. Their work benefits plants, animals, and even humans. Understanding their ecological importance shows why bats matter beyond just being creatures of the night.
These flying mammals support healthy environments. They keep insect numbers low, help flowers grow, and spread seeds. Their actions promote forest growth and crop health.
Pest Control
Bats eat large numbers of insects every night. Many of these insects are pests that damage crops. By eating pests, bats reduce the need for chemical pesticides. This helps farmers save money and protects the environment. Bats keep insect populations in balance naturally.
Pollination
Some bats pollinate flowers while they feed on nectar. They carry pollen from one flower to another. This process helps plants produce fruits and seeds. Many tropical fruits depend on bats for pollination. Without bats, these plants would struggle to reproduce.
Seed Dispersal
Bats also spread seeds through their droppings. They eat fruits and fly long distances. Seeds drop in new places, helping forests grow and recover. This seed dispersal supports biodiversity and creates new habitats. Bats are essential for keeping forests healthy and alive.

Credit: a-z-animals.com
Conservation Efforts
Bats are often misunderstood creatures. They are not rodents but mammals with unique roles in nature. Conservation efforts help protect these important animals. These efforts focus on stopping threats and promoting safe environments for bats.
Threats To Bat Populations
Bats face many dangers today. Habitat loss is a major problem. Trees and caves where bats live are destroyed. Pollution harms the insects bats eat. Diseases like white-nose syndrome kill many bats. Human fear also causes harm. People sometimes destroy bat homes out of fear or misunderstanding.
Protective Measures
Many groups work to save bats. They protect bat habitats by creating reserves. Laws help stop hunting and destroying bat homes. Scientists study bats to learn more about their needs. Bat houses are built to give bats safe places to live. Education helps people understand bats better and respect them.
How To Support Bats
Anyone can help bats in simple ways. Plant native trees and avoid cutting old trees. Avoid using pesticides that kill insects. Put up bat houses in your yard. Learn about bats and share facts with others. Support local bat conservation groups. Small actions can make a big difference for bats.
Credit: www.jcehrlich.com
How Smart Pets Lover Can Help You with Are Bats Rodents
Exploring Bat Facts Beyond Rodent Myths
Understanding whether bats are rodents opens a door to fascinating practical learning opportunities. Since we’ve already explored bat classification and debunked common myths about bats, you might be inspired to dive deeper into their unique features and ecological importance.
For instance, observing how bats contribute to pest control or pollination can enhance your appreciation of their role in nature—something every pet and animal lover can relate to. If you’re a curious pet parent who enjoys sharing facts with family or friends, consider starting a mini wildlife journal or joining local conservation efforts. These activities not only enrich your knowledge but also foster empathy for these misunderstood creatures.
At Smart Pets Lover, our mission is to help you feel confident and connected with all animals, whether it’s your dog or a nighttime visitor like a bat. If you want more trusted insights or have questions about wildlife around your home, feel free to reach out to our community for friendly advice.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Bats Classified As Rodents?
No, bats are not rodents. They belong to the order Chiroptera, while rodents belong to Rodentia. Bats are mammals with wings, capable of true flight, unlike rodents.
How Do Bats Differ From Rodents?
Bats have wings and fly, rodents do not. Bats use echolocation for navigation, rodents rely on smell and sight. Their diets and behaviors also differ significantly.
Why Are Bats Often Mistaken For Rodents?
Bats and rodents are small mammals, leading to confusion. However, bats have wings and fly, while rodents have furred bodies and walk or climb. Their anatomy is distinct.
What Is The Scientific Classification Of Bats?
Bats belong to the order Chiroptera. Rodents belong to the order Rodentia. This classification highlights fundamental differences between the two groups.
Conclusion
Bats are not rodents; they belong to a different group called mammals. They have wings and fly, unlike rodents that only walk or climb. Bats play an important role in nature by eating insects and helping plants grow. Knowing this helps us understand and respect these unique creatures better.
Next time you see a bat, remember it is special and different from mice or rats. Learning about animals can be simple and fun. Keep exploring the natural world around you!




