Male Vs Female Groundhog: Key Differences You Must Know
Have you ever wondered if male and female groundhogs are really that different? You might think they look alike, but there’s more beneath the surface that could surprise you.
Understanding these differences can change how you see these furry creatures and even make your next outdoor encounter more interesting. Keep reading, and you’ll discover fascinating facts about male vs female groundhogs that most people don’t know. This simple insight might just make your next nature walk a little more exciting.

Credit: commons.wikimedia.org
Physical Differences
Male and female groundhogs show clear physical differences. These differences help to tell them apart in the wild. Understanding these traits gives insight into their behavior and roles.
Size And Weight Variations
Male groundhogs are usually larger than females. They weigh more and have a bigger body frame. Females tend to be smaller and lighter. This size difference helps males during mating season.
Fur And Color Patterns
Both males and females have thick, brownish-gray fur. Females’ fur may appear slightly lighter. Males often show denser and coarser fur. Color shades can vary but do not strongly differ by sex.
Distinctive Features
Males have broader heads and stronger jaws. Females have a softer face shape and smaller teeth. Male groundhogs may have more visible scars or marks from fights. These features are subtle but noticeable on close observation.
Behavioral Traits
Groundhogs show clear differences in their behavior based on gender. Male and female groundhogs act differently in many ways. These differences help them survive and live well in their environments. Understanding these behaviors gives us better insight into their lives.
Behavioral traits like territorial habits, social interactions, and activity patterns vary between males and females. These traits affect how they find food, protect themselves, and raise their young. Let’s explore these key behaviors.
Territorial Habits
Male groundhogs usually have larger territories than females. They mark their areas with scent to warn others. Males often defend their space aggressively from rivals. Females keep smaller, more focused territories. Their areas mainly cover places for food and shelter. Both genders avoid overlapping territories to reduce fights.
Social Interactions
Female groundhogs tend to be more social with close family members. They often share burrows with their young. Males are more solitary and avoid other males outside breeding season. They meet females mainly to mate. Social bonds in females help protect the young from danger. Males rely on strength and size to compete for mates.
Activity Patterns
Male groundhogs are more active during early morning and late afternoon. This pattern helps them patrol their large territories. Females spend more time near their burrows, especially when caring for pups. Both males and females hibernate in winter but wake up at different times. These activity differences reduce competition and increase survival chances.
Reproductive Roles
Reproductive roles in groundhogs show clear differences between males and females. Each gender plays unique parts in ensuring the survival of their young. These roles shape their behavior and biology during the breeding period.
Mating Season Behavior
Male groundhogs become more active during mating season. They search widely to find female partners. Males often compete with each other to gain access to females. Females signal readiness by scent and body language. This triggers males to approach and court them carefully.
Nesting And Offspring Care
Female groundhogs build and maintain nests underground. They prepare a safe, warm space for their babies. After birth, females stay close to their young. They feed and protect them until the pups grow stronger. Males usually do not help with nesting or care.
Hormonal Influences
Hormones control groundhog reproductive behaviors and roles. Male testosterone increases aggression and mating drive. Female hormones regulate pregnancy and motherly instincts. These hormonal changes happen at specific times to support reproduction. They ensure each gender fulfills its role effectively.

Credit: www.reddit.com
Habitat Preferences
Male and female groundhogs show differences in where they live. Their habitat choices affect their survival and daily life. Understanding these preferences helps us see how each adapts to the environment.
Both sexes need safe places to rest, raise young, and hide from predators. They choose spots that meet these needs but also fit their behavior and roles.
Burrow Locations
Male groundhogs often build burrows in open areas. These places give them space to move and find mates. Their burrows tend to be larger and more complex.
Female groundhogs prefer quieter, safer spots. They pick burrows with good cover from plants or rocks. These locations protect their young from harm.
Both males and females dig burrows underground. The structure includes entrances, chambers, and tunnels. This design keeps them safe and warm.
Environmental Adaptations
Groundhogs adapt to cold and warm climates differently. Males can travel longer distances to find food. Their larger size helps them survive tough conditions.
Females stay closer to their burrows during harsh weather. They focus on protecting their young and keeping the burrow secure.
Both sexes use their strong claws to dig through soil. This skill helps them create homes in various environments, from forests to fields.
Lifespan And Health
Understanding the lifespan and health of groundhogs helps us know how these animals live. Male and female groundhogs face different health challenges. Their life expectancy also shows some differences. These points give insight into their survival and well-being.
Common Health Issues
Groundhogs often suffer from parasites like ticks and fleas. These can cause itching and skin problems. Both males and females are vulnerable to these pests. Respiratory infections are also common. These infections may make breathing difficult. Injuries from fights or accidents can affect groundhogs too. Males tend to get more injuries because of fighting for mates. Females are more prone to health problems during pregnancy and raising young.
Longevity Differences
Female groundhogs usually live longer than males. Females can live up to 6 years in the wild. Males often live around 4 to 5 years. The shorter life of males links to their riskier behavior. Males fight more and roam wider areas. This increases their chance of injury or death. Females stay closer to their burrows and avoid danger. This careful behavior helps females live longer lives.
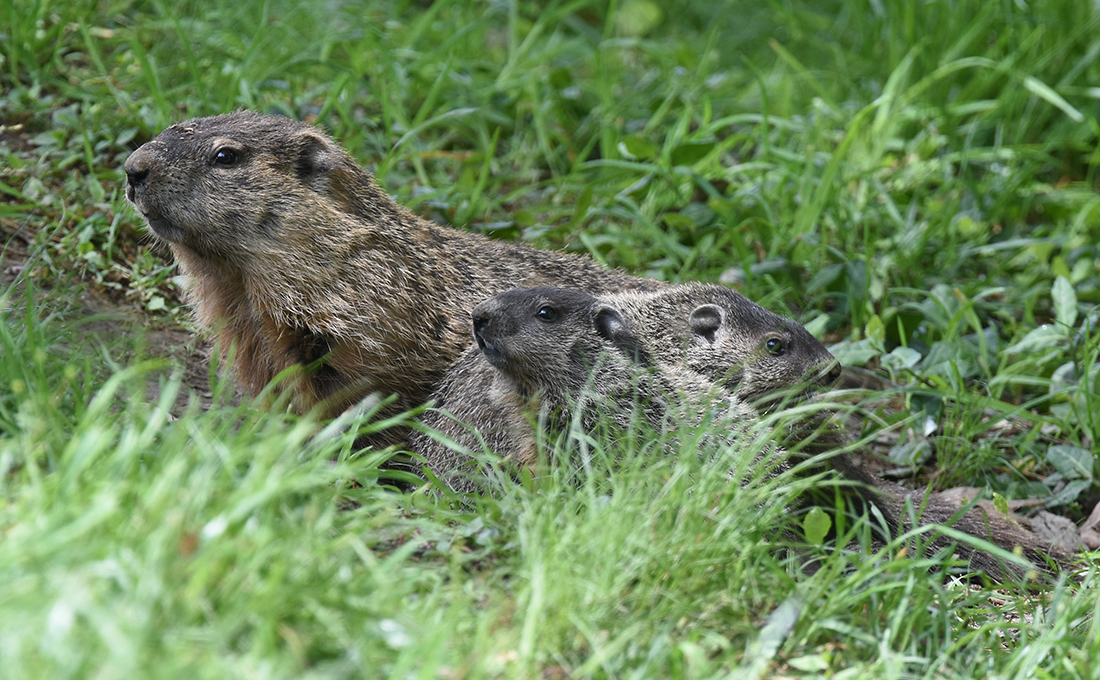
Identifying Male And Female Groundhogs
Identifying male and female groundhogs can be tricky. Both look quite similar in size and color. Yet, some clear signs help tell them apart. Knowing these signs helps in understanding their behavior and roles in nature.
Physical Examination Tips
Male groundhogs tend to be larger and heavier than females. Check the shape of the body; males usually have broader heads. Females may appear slightly slimmer and less bulky.
Look under the tail carefully. Male groundhogs have visible genitalia, while females show nipples on their belly. This is easier to see during the breeding season. Handle them gently and only if necessary.
Behavioral Clues
Males often act more boldly and defend their territory. They roam larger areas compared to females. Females spend more time near their burrows, especially when raising pups.
During mating season, males may follow females closely. Females show nesting behavior and stay hidden with their young. Watching these actions can give strong hints about their sex.

Credit: njaes.rutgers.edu
How Smart Pets Lover Can Help You with Male Vs Female Groundhog
Practical Learning from Male Vs Female Groundhog Differences
Understanding the physical differences and behavioral traits between male and female groundhogs opens a window to appreciating their unique roles in nature. For instance, recognizing how reproductive roles influence female groundhogs’ behavior can deepen your respect for their nurturing instincts and seasonal habits. Observing habitat preferences can also teach us about how these animals adapt to their environments, offering valuable lessons in wildlife coexistence.
As a fellow animal enthusiast, it’s rewarding to connect these insights with responsible wildlife observation and even pet care principles. At Smart Pets Lover, we believe that every discovery—whether about dogs, cats, or wild creatures like groundhogs—helps pet parents feel more confident and connected to animals. If you’re curious about identifying subtle differences or want to share observations, resources like local wildlife centers can be a great support.
Remember, learning about these fascinating creatures not only enriches your knowledge but also nurtures a deeper bond with all animals around you.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Key Differences Between Male And Female Groundhogs?
Male groundhogs are generally larger and more territorial than females. Females focus more on nesting and raising young. Both sexes share similar behaviors like burrowing, but males tend to roam more widely.
How Can You Identify A Male Groundhog From A Female?
Size is a common indicator; males are bigger and bulkier. Males also have more prominent scent glands. Behavioral cues, such as roaming patterns, can help, but visual identification may require close observation.
Do Male And Female Groundhogs Hibernate Differently?
Both male and female groundhogs hibernate in winter. Females often enter hibernation later due to gestation needs. Males typically emerge first in spring to establish territory and find mates.
Which Gender Is More Aggressive In Groundhogs?
Male groundhogs are usually more aggressive, especially during mating season. They defend their territory fiercely. Females tend to be more protective when caring for their young but are less confrontational overall.
Conclusion
Male and female groundhogs share many traits but differ in key ways. Males tend to be larger and more territorial. Females focus on caring for their young and building nests. Both play important roles in their ecosystem. Understanding these differences helps us appreciate groundhogs better.
Nature’s design is simple yet effective. Each gender contributes to the species’ survival. Observing groundhogs can teach us about animal behavior. Small details reveal big stories in wildlife. Groundhogs remind us how life adapts and thrives.