How Do Eels Reproduce
Have you ever wondered how eels reproduce? These mysterious creatures live hidden lives beneath the water’s surface, making their reproduction a fascinating puzzle.
If you’re curious about where eels go to mate, how they find each other, and what happens to their young, you’re in the right place. By the end of this article, you’ll uncover surprising facts about eel reproduction that might just change the way you see these slippery swimmers forever.
Keep reading—you won’t want to miss this!
Eel Reproduction Basics
Eels have a unique and mysterious way of reproducing. Their life cycle is different from many other fish. Most eels live in fresh water but travel long distances to breed in the ocean. This journey is called spawning migration.
Scientists have studied eel reproduction for many years. It is hard to observe because eels spawn far from shore. Understanding their basics helps us learn more about their life and survival.
Where Do Eels Reproduce?
Eels reproduce in the deep ocean, far from where they live most of their lives. The most famous place is the Sargasso Sea in the Atlantic Ocean. This area is full of floating seaweed and provides a safe place for baby eels to start growing.
How Do Eels Find Each Other?
Eels use their sense of smell to find mates during their migration. They travel thousands of miles guided by the ocean’s currents. This long trip helps them meet in the same spawning area to reproduce.
What Happens During Spawning?
During spawning, eels release eggs and sperm into the water. Fertilization happens outside their bodies. After this, adult eels die, and the eggs drift with the ocean currents.
How Do Baby Eels Grow?
Baby eels, called leptocephali, look very different from adults. They are flat and transparent. They float in the ocean for many months before moving to freshwater or coastal areas to grow into adults.
Credit: www.animalwised.com
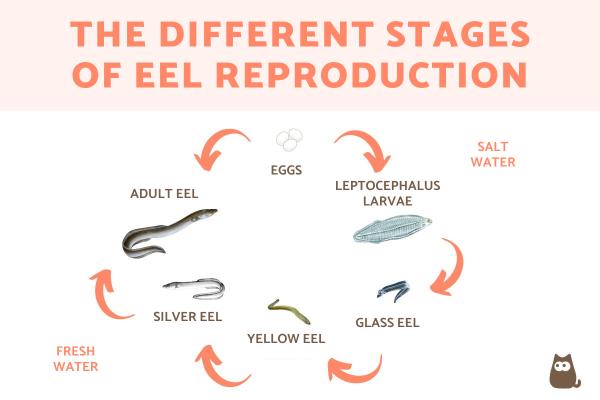
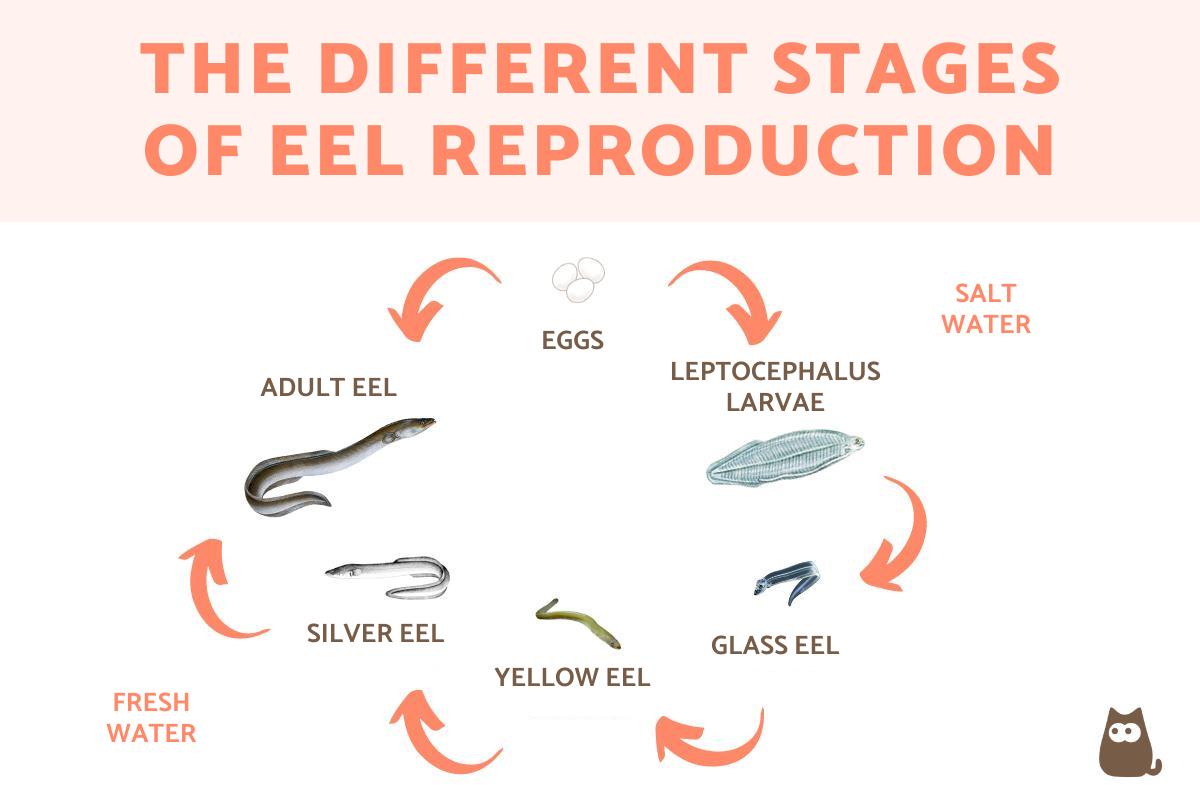
Life Cycle Stages
The life cycle of eels is unique and fascinating. It includes several important stages, each playing a key role in their growth and reproduction. Understanding these stages helps us learn how eels survive and thrive in different environments. The journey begins in the ocean and ends in fresh waters, showing a remarkable transformation.
Larval Phase
Eels start their life as tiny larvae called leptocephali. These larvae are flat and transparent. They drift with ocean currents for months or even years. During this time, they feed on small particles in the water. This stage is crucial for their growth and survival. The larvae slowly move closer to coastal areas as they develop.
Glass Eel Transition
After the larval phase, eels enter the glass eel stage. They become small and clear, like glass. This change happens as they approach freshwater rivers and estuaries. Glass eels begin to swim against the current. This migration is important for reaching their new habitats. At this stage, they start to look more like adult eels.
Adult Maturation
Once in fresh water, eels grow into adults. They change color and develop stronger bodies. Adults live in rivers, lakes, or coastal waters for many years. During this time, they prepare to return to the ocean to reproduce. Adult eels undergo physical changes to swim long distances. This final stage completes the life cycle and begins it anew.
Spawning Migration
Eels undergo a fascinating spawning migration that defines their life cycle. This journey is long and full of challenges. It leads them from freshwater or coastal areas to deep ocean locations. These areas serve as their spawning grounds, where reproduction happens.
The migration is a crucial event. It ensures the survival of the next eel generation. Understanding this migration reveals much about eel behavior and biology.
Migration Triggers
Eels start their migration due to changes in water temperature and daylight. These natural signals tell them it is time to move. Their bodies also change, preparing for the long trip ahead. Energy stores increase, and their eyes grow bigger to see in deep water. Instinct drives them toward the ocean’s depths.
Journey To Spawning Grounds
The journey can stretch thousands of miles across oceans. Eels swim mostly at night, avoiding predators and strong currents. They travel alone but follow similar routes each year. The famous Sargasso Sea in the Atlantic Ocean is a key spawning site. Here, eels release their eggs and sperm before dying. The next generation hatches and drifts back to coastal waters to grow.

Credit: teara.govt.nz
Spawning Behavior
Eels have a unique and mysterious spawning behavior. It is a key part of their life cycle. This behavior happens once in their lifetime. Eels leave their freshwater homes and travel to the ocean. There, they spawn and complete their life journey.
Spawning Location
Eels spawn far from the coast. They gather in deep ocean waters. The exact spot is usually the Sargasso Sea. This place is calm and has floating seaweed. The seaweed offers protection for the eggs and larvae. Eels travel thousands of miles to reach this site.
Mating Process
Eels do not form pairs. They release eggs and sperm into the water. This process is called external fertilization. It happens at night. Females release thousands of eggs. Males release sperm to fertilize them. The eggs then drift with ocean currents. Larvae hatch and start a long journey back to freshwater.
Challenges In Reproduction
Eels face many challenges during reproduction. Their journey to spawn is long and difficult. Many factors make it hard for eels to reproduce successfully. These challenges affect eel populations worldwide.
Environmental Threats
Environmental changes harm eel reproduction. Water pollution damages their breeding habitats. Changes in water temperature confuse their migration routes. Loss of clean rivers limits safe spawning areas. Climate change disrupts the timing of reproduction. These threats reduce the chances of eel survival.
Human Impact
Human activities create many problems for eels. Dams block their migration paths to breeding grounds. Overfishing lowers the number of mature eels. Illegal fishing targets young eels, stopping growth. Habitat destruction removes important breeding sites. Pollution from factories and farms poisons the water. These impacts make eel reproduction even harder.
Credit: www.animalwised.com
Scientific Discoveries
Scientists have long been curious about how eels reproduce. These mysterious creatures travel vast distances in the ocean. Tracking their reproductive habits has been difficult. New scientific tools and studies help reveal their secrets. Research now sheds light on where and how eels spawn. This knowledge changes what we know about their life cycle.
Tracking Techniques
Scientists use tiny tracking devices to follow eel movements. These devices send location data from deep ocean areas. Satellite tags help monitor long migrations. Researchers study changes in eel behavior during spawning seasons. Tracking shows eels swim thousands of miles to breeding sites. This method provides real-time data about eel routes and timing. It helps pinpoint where eels reproduce in the ocean.
Recent Research Findings
New studies confirm eels spawn in specific ocean zones. Most eels reproduce in the Sargasso Sea. Scientists discovered larvae drift with ocean currents after spawning. Research reveals eels produce millions of eggs during reproduction. Findings show eels do not return to freshwater after spawning. Scientists learn eels have a single reproductive event before dying. These discoveries improve conservation efforts for eel populations.
How Smart Pets Lover Can Help You with How Do Eels Reproduce
Exploring Eel Reproduction: Practical Learning for Curious Minds
Understanding how eels reproduce opens a fascinating window into nature’s mysteries, especially when you consider their complex spawning migration and unique life cycle stages. For anyone curious about aquatic life or looking to deepen their knowledge, these topics offer rich opportunities to connect theory with real-world observation.
One practical way to engage is by following scientific discoveries about eel spawning behavior, which often involve tracking their incredible journey back to the Sargasso Sea. You might explore documentaries, join local aquatic workshops, or even participate in citizen science projects focused on freshwater ecosystems. These experiences not only enhance your understanding but also build a deeper appreciation for the challenges eels face during reproduction.
At Smart Pets Lover, we believe that learning about all creatures—whether your pet dog or a wild eel—helps foster empathy and responsible care. If you want to dive deeper into eel biology or share your findings, consider reaching out to local marine biology centers or online forums dedicated to fish research. It’s a wonderful way to connect with fellow enthusiasts and keep your passion for animals thriving.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Eels Find Their Spawning Grounds?
Eels migrate thousands of miles to the Sargasso Sea to spawn. They use magnetic fields and ocean currents to navigate accurately.
When Do Eels Reproduce During Their Lifecycle?
Eels reproduce once at the end of their lifecycle, typically after 6-20 years. This event happens during their oceanic migration.
What Happens During Eel Spawning And Reproduction?
Eels release eggs and sperm simultaneously in deep ocean waters. Fertilized eggs drift and hatch into larvae, starting their growth journey.
Why Is Eel Reproduction Still A Mystery?
Eel spawning occurs deep in the ocean, making it hard to observe. Scientists continue researching to fully understand their reproductive behaviors.
Conclusion
Eels have a unique and fascinating way to reproduce. They travel long distances to the ocean to spawn. After laying eggs, young eels grow and return to freshwater. This life cycle shows nature’s wonder and mystery. Understanding eel reproduction helps us protect these creatures.
Their journey reminds us how life adapts and survives. Eels play an important role in their ecosystems. Watching their life story teaches us about nature’s balance. Simple yet amazing.






